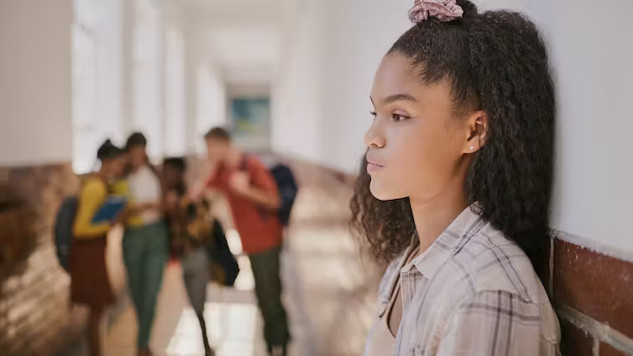
Spreading rumors about others is one form of bullying. LumiNola/E+ via Getty Images
Being bullied can make your life miserable, and decades of research prove it: Bullied children and teens are at risk for anxiety, depression, dropping out of school, peer rejection, social isolation and self-harm.
Adults can be bullied too, often at a job, and they may suffer just as much as kids do.
I’m a professor who studies child and adolescent development. That includes learning how people become bullies – and how they can be stopped.
First, let’s define what bullying is: It’s mean-spirited, harmful behavior by someone with more power or status – like a popular kid at school or a supervisor at work – who repeatedly picks on, harasses, irritates or injures a person with less power or status.
Bullying can take many forms – physical, like pushing, shoving and hitting; relational, such as spreading rumors, keeping somebody out of a friend group or just rude remarks; or sexual harassment and stalking behavior.
Sometimes, bullies target someone because of their race, religion, sexual orientation or appearance. People from the LGBTQ+ community, or who are overweight, or with a physical or developmental disability are more likely to be bullied. As a result, they may develop mental health problems, including depression, anxiety and self-harming behavior.
So why do bullies do it?
People learn how to bully others early on through what psychologists call modeling and social learning. This means bullies see other people bullying and they essentially model, or copy, this aggressive behavior.
Media is a big culprit here. When mean or violent conduct is glamorized and gamified in music, video games, TV and movies, bullies will imitate what they see and hear, especially if it seems cool or if it’s rewarded.
Family is also an influence. If children grow up in a home without kindness and closeness, but with plenty of physical punishment and heavy conflict – including parents fighting with each other – then children view this behavior as acceptable. They can go on to treat their peers this way.
A similar thing happens when a kid falls into a group of friends who are bullies; they become more likely to bully others themselves. To say it another way, they bully because they think it makes them look cool in front of their friends.
And bullies bully for lots of other reasons. Some do it because it makes them feel better about themselves when they put other people down. Other bullies discovered that force and intimidation worked for them in the past, so it’s a go-to strategy to get what they want. Still others simply have difficulty controlling themselves and can’t calm down when they’re angry.
And with some bullies, it’s just a way to get ahead. For instance, an adult bully in the workplace may spread an embarrassing rumor about a co-worker to keep a rival from being promoted.
How to handle bullies
Fortunately, there are lots of ways to stop a bully.
If you’re a child or teenager, talk about what has happened with a trusted adult – a parent, teacher, principal or counselor. They will help you figure out your next move. Schools are familiar with this sort of problem; they have policies in place to protect victims of bullying.
If you’re an adult who has been bullied in the workplace, talk to your human resources department or a neutral supervisor who can advise you on next steps. You are also legally protected – employment laws prohibit harassment and discriminatory behavior.
Whatever your age, it’s a good idea to talk to friends or family members who may not be involved in the incident but who will offer support. Engaging in coping activities – like exercising, or relaxing with a walk – may also help.
And a final word: Bullying is not acceptable. It’s not just “kids being kids,” or that you’re “too sensitive.” If a bully is bothering you, don’t try to handle it alone – getting help is the way to get through.
Sara Goldstein, Professor of Human Development, University of Delaware
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Related Books:
Atomic Habits: An Easy & Proven Way to Build Good Habits & Break Bad Ones
by James Clear
Atomic Habits provides practical advice for developing good habits and breaking bad ones, based on scientific research on behavior change.
Click for more info or to order
The Four Tendencies: The Indispensable Personality Profiles That Reveal How to Make Your Life Better (and Other People's Lives Better, Too)
by Gretchen Rubin
The Four Tendencies identifies four personality types and explains how understanding your own tendencies can help you improve your relationships, work habits, and overall happiness.
Click for more info or to order
Think Again: The Power of Knowing What You Don't Know
by Adam Grant
Think Again explores how people can change their minds and attitudes, and offers strategies for improving critical thinking and decision making.
Click for more info or to order
The Body Keeps the Score: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of Trauma
by Bessel van der Kolk
The Body Keeps the Score discusses the connection between trauma and physical health, and offers insights into how trauma can be treated and healed.
Click for more info or to order
The Psychology of Money: Timeless lessons on wealth, greed, and happiness
by Morgan Housel
The Psychology of Money examines the ways in which our attitudes and behaviors around money can shape our financial success and overall well-being.





















