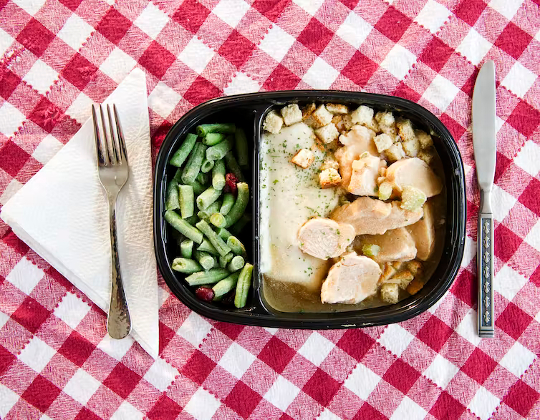
Surprisingly, even packaged foods that contain healthy components can qualify as ultra-processed. Jamie Grill Photography/Tetra Images via Getty Images
Scientists have known for years that unhealthy diets – particularly those that are high in fat and sugar – may cause detrimental changes to the brain and lead to cognitive impairment.
Many factors that contribute to cognitive decline are out of a person’s control, such as genetics and socioeconomic factors. But ongoing research increasingly indicates that a poor diet is a risk factor for memory impairments during normal aging and increases the risk of developing Alzheimer’s disease.
But when evaluating how some diets may erode brain health as we age, research on the effects of consuming minimally processed versus ultra-processed foods has been scant – that is, until now.
Two recent large-scale studies suggest that eating ultra-processed foods may exacerbate age-related cognitive decline and increase the risk of developing dementia. In contrast, another recent study reported that ultra-processed food consumption was not associated with worse cognition in people over 60.
Although more research is needed, as a neuroscientist who researches how diet can influence cognition later in life, I find that these early studies add a new layer for considering how fundamental nutrition is to brain health.
Lots of ingredients, minimal nutrition
Ultra-processed foods tend to be lower in nutrients and fiber and higher in sugar, fat and salt compared to unprocessed or minimally processed foods. Some examples of ultra-processed foods include soda, packaged cookies, chips, frozen meals, flavored nuts, flavored yogurt, distilled alcoholic beverages and fast foods. Even packaged breads, including those high in nutritious whole grains, qualify as ultra-processed in many cases because of the additives and preservatives they contain.
Another way to look at it: You are not likely to find the ingredients that make up most of these foods in your home kitchen.
But don’t confuse ultra-processed with processed foods, which still retain most of their natural characteristics, although they’ve undergone some form of processing – like canned vegetables, dried pasta or frozen fruit.
A look at three categories of foods.
Parsing the research
In a December 2022 study, researchers compared the rate of cognitive decline over approximately eight years between groups of people that consumed different amounts of ultra-processed foods.
At the beginning of the study, over 10,000 participants living in Brazil reported their dietary habits from the previous 12 months. Then, for the ensuing years, the researchers evaluated the cognitive performance of the participants with standard tests of memory and executive function.
Those who ate a diet containing more ultra-processed foods at the start of the study showed slightly more cognitive decline compared with those that ate little to no ultra-processed foods. This was a relatively modest difference in the rate of cognitive decline between experimental groups. It is not yet clear if the small difference in cognitive decline associated with higher consumption of ultra-processed foods will have a meaningful effect at the level of an individual person.
The second study, with about 72,000 participants in the U.K., measured the association between eating ultra-processed foods and dementia. For the group eating the highest amounts of ultra-processed foods, approximately 1 out of 120 people were diagnosed with dementia over a 10-year period. For the group that consumed little to no ultra-processed foods, this number was 1 out of 170.
Research examining the relationship between health and ultra-processed foods uses the NOVA classification, which is a categorization system based on the type and extent of industrial food processing. Some nutritionists have criticized the NOVA classification for not having clear definitions of food processing, which could lead to misclassification. They also argue that the potential health risks from consuming ultra-processed foods could be explained by low levels of fiber and nutrients and high levels of fat, sugar and salt in the diet rather than the amount of processing.
Many ultra-processed foods are high in additives, preservatives or coloring agents, while also having other features of an unhealthy diet, such as being low in fiber and nutrients. Thus, it is unclear if eating food that has undergone more processing has an additional negative impact on health beyond low diet quality.
For example, you could eat a burger and fries from a fast food chain, which would be high in fat, sugar and salt as well as being ultra-processed. You could make that same meal at home, which could also be high in fat, sugar and salt but would not be ultra-processed. More research is needed to determine whether one is worse than the other.
Brain-healthy diets
Even when the processes that lead to dementia are not occurring, the aging brain undergoes biochemical and structural changes that are associated with worsening cognition.
But for adults over the age of 55, a healthier diet could increase the likelihood of maintaining better brain function. In particular, the Mediterranean diet and ketogenic diet are associated with better cognition in advanced age.
The Mediterranean diet emphasizes the consumption of plant-based foods and healthy fats, like olive oil, seeds and nuts. The ketogenic diet is high in fat and low in carbohydrates, with the primary fiber source being from vegetables. Both diets minimize or eliminate the consumption of sugar.
Our research and the work of others show that both diets can reverse some of these changes and improve cognitive function – possibly by reducing harmful inflammation.
Although inflammation is a normal immune response to injury or infection, chronic inflammation can be detrimental to the brain. Studies have shown that excess sugar and fat can contribute to chronic inflammation, and ultra-processed foods might also exacerbate harmful inflammation.
Another way that diet and ultra-processed foods may influence brain health is through the gut-brain axis, which is the communication that occurs between the brain and the gut microbiome, or the community of microorganisms that live in the digestive tract.
Not only does the gut microbiome help with digestion, but it also influences the immune system, while producing hormones and neurotransmitters that are critical for brain function.
Studies have shown that the ketogenic and Mediterranean diets change the composition of microorganisms in the gut in ways that benefit the person. Ultra-processed food consumption is also associated with alterations in the type and abundance of gut microorganisms that have more harmful effects.
There’s a war going on in your gut: good bacteria versus bad bacteria.
The uncertainties
Disentangling the specific effects of individual foods on the human body is difficult, in part because maintaining strict control over people’s diets to study them over long periods of time is problematic. Moreover, randomized controlled trials, the most reliable type of study for establishing causality, are expensive to carry out.
So far, most nutritional studies, including these two, have only shown correlations between ultra-processed food consumption and health. But they cannot rule out other lifestyle factors such as exercise, education, socioeconomic status, social connections, stress and many more variables that may influence cognitive function.
This is where lab-based studies using animals are incredibly useful. Rats show cognitive decline in old age that parallels humans. It’s easy to control rodent diets and activity levels in a laboratory. And rats go from middle to old age within months, which shortens study times.
Lab-based studies in animals will make it possible to determine if ultra-processed foods are playing a key role in the development of cognitive impairments and dementia in people. As the world’s population ages and the number of older adults with dementia increases, this knowledge cannot come soon enough.![]()
About The Author
Sara N. Burke, Associate Professor of Neurobiology and Cognitive Aging, University of Florida
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Related Books:
Salt, Fat, Acid, Heat: Mastering the Elements of Good Cooking
by Samin Nosrat and Wendy MacNaughton
This book offers a comprehensive guide to cooking, focusing on the four elements of salt, fat, acid, and heat and offering insights and techniques for creating delicious and well-balanced meals.
Click for more info or to order
The Skinnytaste Cookbook: Light on Calories, Big on Flavor
by Gina Homolka
This cookbook offers a collection of healthy and delicious recipes, focusing on fresh ingredients and bold flavors.
Click for more info or to order
Food Fix: How to Save Our Health, Our Economy, Our Communities, and Our Planet--One Bite at a Time
by Dr. Mark Hyman
This book explores the links between food, health, and the environment, offering insights and strategies for creating a healthier and more sustainable food system.
Click for more info or to order
The Barefoot Contessa Cookbook: Secrets from the East Hampton Specialty Food Store for Simple Entertaining
by Ina Garten
This cookbook offers a collection of classic and elegant recipes from the beloved Barefoot Contessa, focusing on fresh ingredients and simple preparation.
Click for more info or to order
How to Cook Everything: The Basics
by Mark Bittman
This cookbook offers a comprehensive guide to cooking basics, covering everything from knife skills to basic techniques and offering a collection of simple and delicious recipes.






















