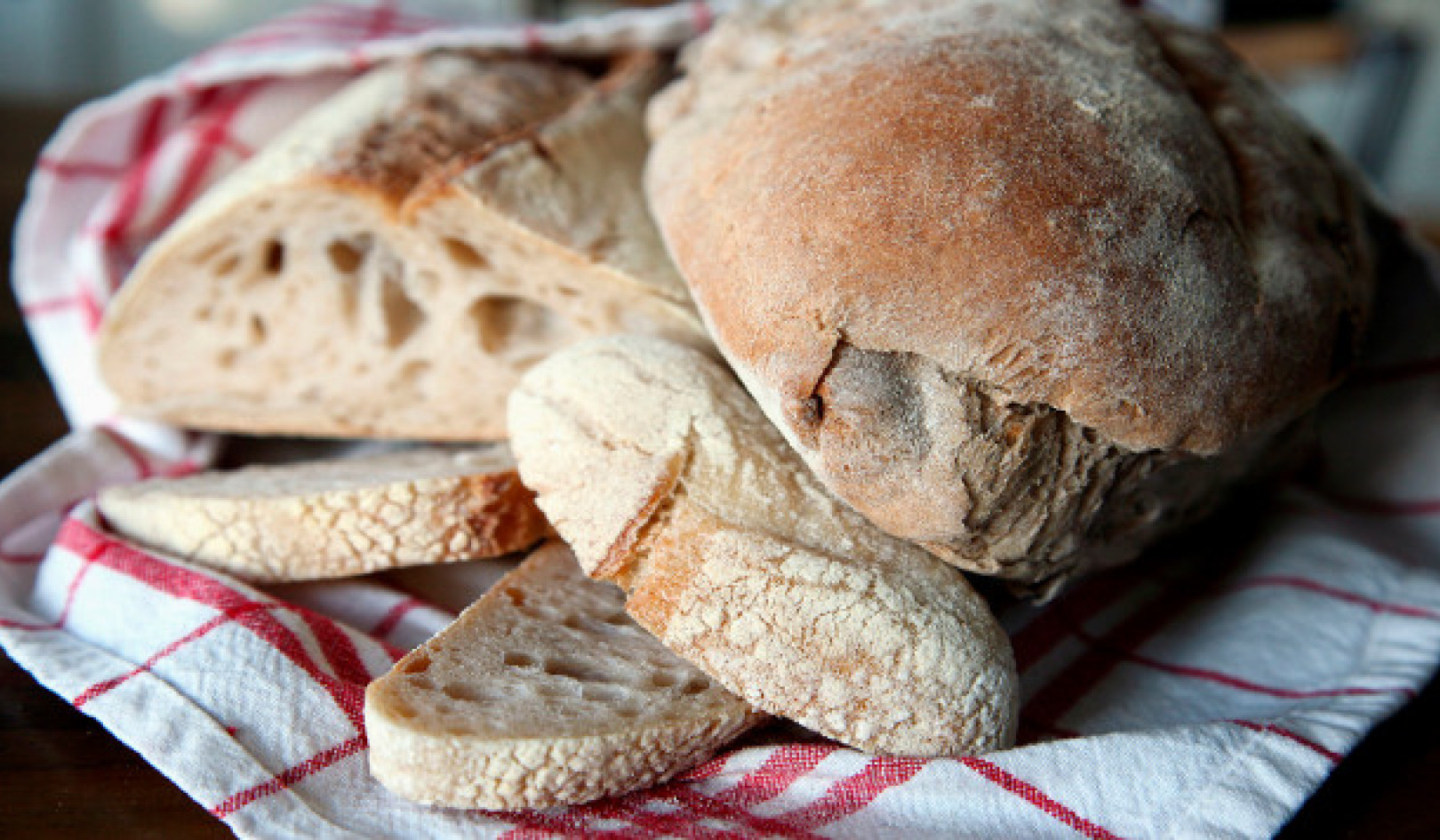
Have you found suspicious webbing on your dried foods? Shutterstock
Has your home recently been overrun by tiny grey moths, flapping erratically around your kitchen? Spotted some suspicious webs in a cereal box? You might be sharing your dried food with pantry moths (Plodia interpunctella).
Although several species of moth can live and breed in our homes, the pantry moth (also known as the “Indian meal moth”) is one of the most common unwanted moth-guests.
Pantry moths are found on every continent except Antarctica. They feed on rice, grains, flour, pasta, cereals, dried fruits, spices, seeds, nuts and other dried food. Their fondness for dried foods makes them a major pest in food storage facilities.
So how did they get in your house – and what can you do to get rid of them?
Large Amounts Of Silk Webbing And Faeces
Like other moths, pantry moths have four distinct life stages: egg, caterpillar, pupae and adult.
The first sign of a pantry moth infestation is often the sight of adult moths flying in an erratic, zig-zag path around our kitchens.
Pantry moth adults have grey-coloured wings with bronze or tan bands near the wing tips.
Although they can be annoying, adult moths do not feed at all. The trouble arises when female moths lay their eggs in or around our food. The tiny eggs hatch into barely visible cream-coloured caterpillars small enough to crawl into poorly sealed food containers. There, they begin to feed.
As they grow, caterpillars produce large amounts of silk webbing and faeces, both of which can contaminate food.
Once a caterpillar reaches its full size, it leaves the food in search of a safe space to make a cocoon, usually a crack, container lid, crevice or corner. Sometimes they turn up in the hinges of a pantry door.
A few weeks later, an adult moth emerges from the cocoon, ready to start the cycle again.

Shutterstock
How Did Pantry Moths Get In My House?
Unfortunately, it’s likely you brought them home yourself. Although pantry moths can enter via doors and windows, most infestations probably start when we inadvertently bring home eggs and caterpillars in our dried foods.
Kitchens full of unsealed containers and spilled food create an irresistible smorgasbord for female moths looking for the ideal place to lay eggs.
Like many insects, pantry moths develop more quickly at warmer temperatures.
At warmer temperatures, females also lay more eggs and caterpillars are more likely to survive to adulthood.
But prolonged exposure to temperatures above 40? are lethal to eggs and caterpillars.
While pantry moths can be found at any time of the year, the warm temperatures of late spring and early summer are often perfect for supporting rapid population growth.
How Do I Get Rid Of Pantry Moths?
First, eliminate their sources of food. Dry goods should be stored in sealed, airtight containers with tight-fitting lids.
To prevent eggs and caterpillars from hitchhiking in on purchases, place dried foods in the freezer for three to four days; this should kill any eggs and caterpillars that may be present.
If you already have an infestation, carefully inspect all potential food sources including spices, cereals, grains, dry pet foods, pasta, seeds, nuts, tea, dried flowers and dried fruit.
Pantry moth caterpillars are hard to see; look for the silken webbing they produce, which can cause food grains to clump together. These webbed clumps are often more conspicuous than the caterpillars themselves.
Infested foods should either be discarded or placed in the freezer for three to four days to kill eggs and caterpillars.
Clean up and discard any spilled foods on shelves, under toasters or behind storage containers. Even small amounts of food can support thriving caterpillar populations
Caterpillars can travel considerable distances to find a safe place to make a cocoon, so make sure to check shelves, walls, crevices and ceilings. Moth cocoons can be removed by wiping with a damp cloth or with a vacuum cleaner.
Cleaning and proper food storage are the best ways to end a pantry moth outbreak. Sticky pantry moth traps are commercially available and can be used to monitor and reduce the moth population.
Pantry moth traps – triangular cardboard covered with a thick sticky glue – are baited with a chemical that mimics the smell of a female pantry moth.
Males are attracted to the trap and become hopelessly stuck to the glue. Since sticky traps only target males, traps are unlikely to stop an outbreak on their own; always use them with proper food storage and careful cleaning.
Insecticide sprays are unlikely to be effective as pantry moth caterpillars and eggs are protected within food containers. Pantry moths are also resistant to a range of insecticides, rendering them ineffective. Insecticides should never be applied on or near food.
What if I ate some pantry moth eggs or larvae?
While it can be disconcerting to find tiny caterpillars in the cereal you’ve been enjoying all week, accidentally eating pantry moth caterpillars is unlikely to cause any health problems.
Given how common they are in stored food, you’ve probably already unknowingly consumed many moth eggs and larvae.
Thank goodness caterpillars are generally an excellent source of protein!![]()
About The Author
Tanya Latty, Associate professor, University of Sydney
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Related Books:
Salt, Fat, Acid, Heat: Mastering the Elements of Good Cooking
by Samin Nosrat and Wendy MacNaughton
This book offers a comprehensive guide to cooking, focusing on the four elements of salt, fat, acid, and heat and offering insights and techniques for creating delicious and well-balanced meals.
Click for more info or to order
The Skinnytaste Cookbook: Light on Calories, Big on Flavor
by Gina Homolka
This cookbook offers a collection of healthy and delicious recipes, focusing on fresh ingredients and bold flavors.
Click for more info or to order
Food Fix: How to Save Our Health, Our Economy, Our Communities, and Our Planet--One Bite at a Time
by Dr. Mark Hyman
This book explores the links between food, health, and the environment, offering insights and strategies for creating a healthier and more sustainable food system.
Click for more info or to order
The Barefoot Contessa Cookbook: Secrets from the East Hampton Specialty Food Store for Simple Entertaining
by Ina Garten
This cookbook offers a collection of classic and elegant recipes from the beloved Barefoot Contessa, focusing on fresh ingredients and simple preparation.
Click for more info or to order
How to Cook Everything: The Basics
by Mark Bittman
This cookbook offers a comprehensive guide to cooking basics, covering everything from knife skills to basic techniques and offering a collection of simple and delicious recipes.
Click for more info or to order