Pro-resistance social media pages share photos of graffiti like this. Provided by Michaela Grancayova and Aliaksei Kazharski.
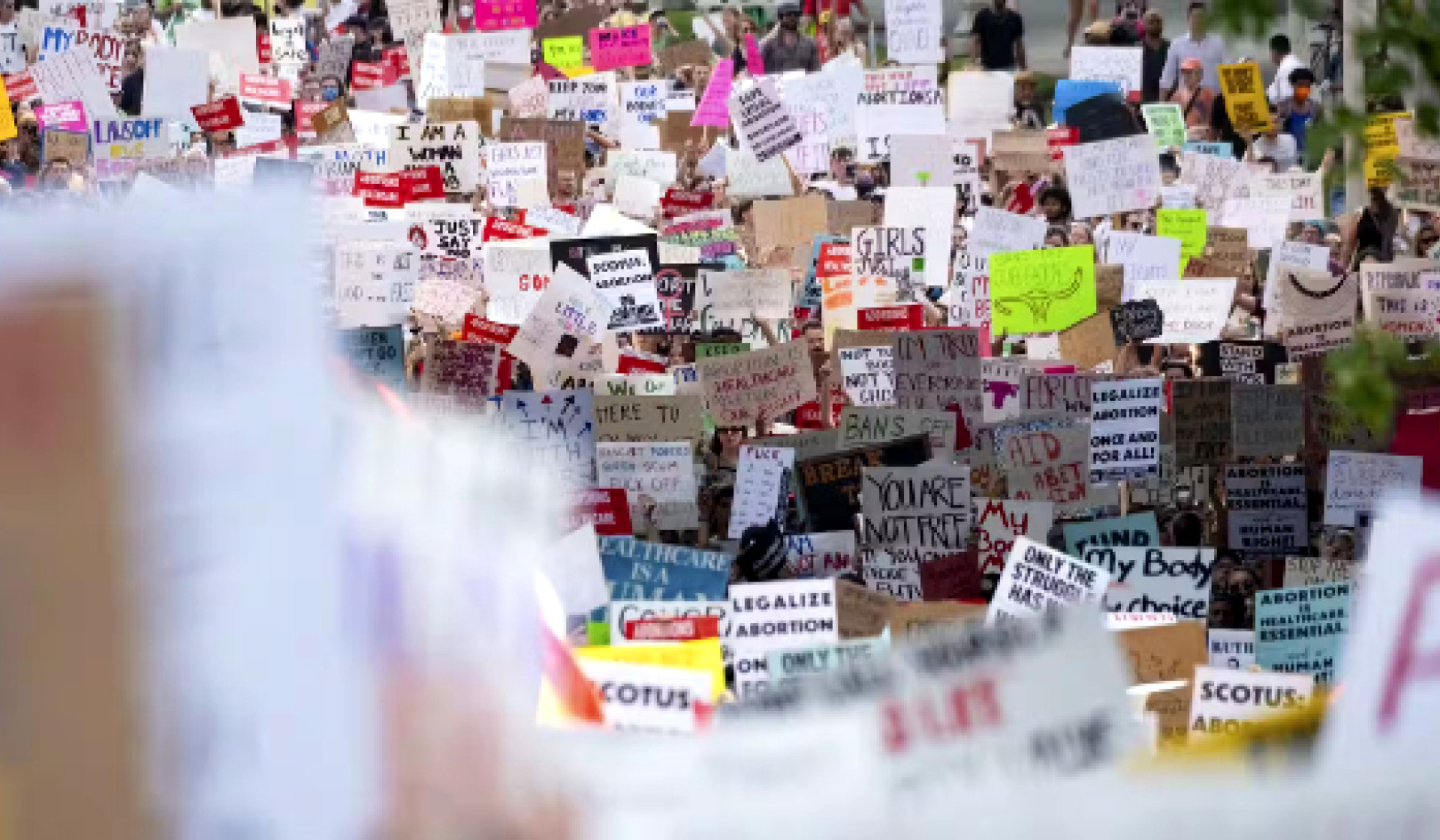
Modern protest movements, like the ongoing protests in Iran, often center around women who have been killed or harmed by agents of authoritarian governments. While it can be easy to chalk up this consistent, state-sponsored abuse of women to simple sexism, researchers say there is a deeper story at play.
Authoritarian regimes often lack a coherent underlying ideology. So to fill that gap, many leaders turn to discrimination, using gender, race or sexuality to vilify opponents and generate support. As a result, pushback against gender as a tool of oppression has taken on a visual and artistic component as protests have entered the social media age.
In this episode of The Conversation Weekly, we speak to three experts who have studied protests and the role of gendered ideology, images and social media as tools of resistance as well as of oppression.
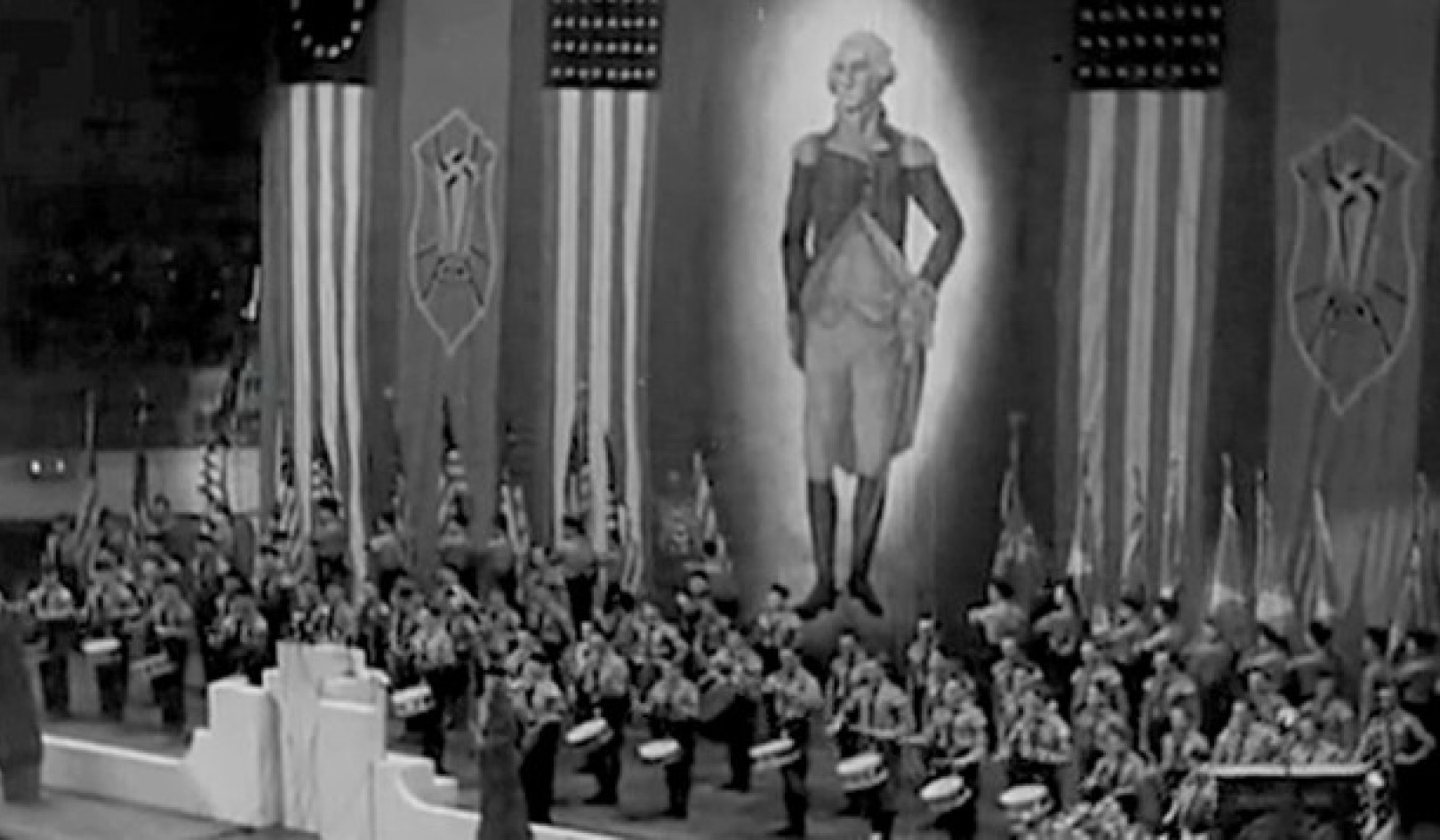
In August 2020, Belarus erupted into unrest after Alexander Lukashenko, the longtime authoritarian leader of the country, won the presidency for the fifth time in an election few considered free or fair.
“There had never been so many people out in the streets before – hundreds of thousands in a country of less than 10 million,” says Aliaksei Kazharski. Kasharski researches international politics and security at Charles University in Prague, in the Czech Republic. He himself is Belarusian.

Belarusian people rose up in massive protests after Alexander Lukashenko was reelected to the presidency in 2020. Ulf Mauder/picture alliance via Getty Images
Michaela Grancayova is a researcher who focuses on language and politics, particularly in the Middle East, and was studying at the same university as Kazharski in 2020. As she was watching the protests in Belarus unfold, Grancayova noticed some striking similarities to the Arab Spring, her own area of research. “The regimes in both countries were relying on the traditional gender images, images of how the ideal woman should behave and should look like,” she explains. “Or how an ideal man should look like, should behave – in this case, hegemonic masculinity.”
“These ideas of hegemonic masculinity and gender basically substitute for an official ideology, which is missing from those regimes,” Kazharski explains. “And in a society that’s more or less traditionalist, this image of a strong leader, a macho, real man actually appeals to many people.”
Not only were there similarities between Lukashenko and Hosni Mubarak, the Egyptian leader who was overthrown during the Arab Spring, Grancayova noticed that the protest movements of both countries fought against these gendered ideologies in much the same fashion, too.
One prominent theme was an idea the researchers call the iconization of victimhood. “There were people who were tortured and humiliated by the regimes, and they were meant to be turned into the victims,” explains Grancayova. “But in reality the people who took part in the protest turned them into heroes and visual icons.”
In both Egypt and Belarus, protesters turned to social media to distribute images of the bloodied martyrs or share images of graffiti or other symbolic visuals.
As a response, both the Egyptian and Belarusian governments tried to squash the social media branches of the protests. As Kazharski explains, Lukashenko “did try to shut down the internet in 2020 for a couple of days but then realized it was way too costly.” Instead, agents of the regime went door to door, searching laptops and phones and torturing those who wouldn’t give up their passwords.
Women’s movements in Iran
These same themes of gender and weaponized social media are playing out today, too, in the ongoing protests in Iran.
Since Mahsa Amini, a 22-year-old Iranian woman, was killed by the Morality Police in fall of 2022, Iran has been enveloped in protests. The movement, called “Woman, Life, Freedom” is in many ways focused, as the name suggests, on restoring the freedoms of women, who have severely limited by the Iranian government.
Parichehr Kazemi is a Ph.D. candidate at the University of Oregon, in the US, where she studies women’s resistance movements across the Middle East with a focus on the use of images on social media.
Previous women’s movements in Iran, like My Stealthy Freedom, where women posted photos of themselves without hijabs in public places, were often centered around images. Kazemi explains that after 2009, “images were birthed because of a very repressive environment under the Islamic Republic that didn’t really give women other opportunities to express dissent.”
When protests erupted in late 2022 after the Morality Police killed Amini, videos of massive crowds and clashes between police and protesters flooded social media. As Kazemi followed the protests on social media, she began seeing more representational imagery emerge. “Over time, it’s not just images of tons of women running from security forces in the streets,” she says. “You see women cutting their hair. You see girls in the streets without their veils. You see them burning their hijabs. You see them dancing in circles. This isn’t something that we’ve seen under the Islamic Republic.”
Under a regime where public protesting can get you killed, Kazemi says, “Images have become a way for people to continue showing the world what’s happening in Iran.”
As in Belarus and Egypt, the Iranian government has been cracking down on social media as a tool of resistance. Among the debates over whether social media is generally a force for resistance or a tool of state control, Kazemi had a bigger-picture perspective. “Social media is embedded within our lifestyles, and we’ll figure out a way to use it as an extension of ourselves. But regimes will also use it as an extension of themselves.”
About The Author
Daniel Merino, Associate Science Editor & Co-Host of The Conversation Weekly Podcast, The Conversation and Nehal El-Hadi, Science + Technology Editor & Co-Host of The Conversation Weekly Podcast, The Conversation
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Related Books:
On Tyranny: Twenty Lessons from the Twentieth Century
by Timothy Snyder
This book offers lessons from history for preserving and defending democracy, including the importance of institutions, the role of individual citizens, and the dangers of authoritarianism.
Click for more info or to order
Our Time Is Now: Power, Purpose, and the Fight for a Fair America
by Stacey Abrams
The author, a politician and activist, shares her vision for a more inclusive and just democracy and offers practical strategies for political engagement and voter mobilization.
Click for more info or to order
How Democracies Die
by Steven Levitsky and Daniel Ziblatt
This book examines the warning signs and causes of democratic breakdown, drawing on case studies from around the world to offer insights into how to safeguard democracy.
Click for more info or to order
The People, No: A Brief History of Anti-Populism
by Thomas Frank
The author offers a history of populist movements in the United States and critiques the "anti-populist" ideology that he argues has stifled democratic reform and progress.
Click for more info or to order
Democracy in One Book or Less: How It Works, Why It Doesn't, and Why Fixing It Is Easier Than You Think
by David Litt
This book offers an overview of democracy, including its strengths and weaknesses, and proposes reforms to make the system more responsive and accountable.