- By Kieran Cooke

Agricultural scientists are linking several pests and diseases affecting British farming with climate change, posing problems for both livestock and crops.
- By Tim Radford

Although hundreds of the world’s glaciers are shrinking fast, far more are losing ice much more slowly, new research has established. But it shows that, almost everywhere, the glaciers are in retreat.
Our society's addiction to fossil fuels is not only polluting our skies and wreaking havoc on our climate - it's also threatening to kill one of mankind's most precious resources.
- By Tim Radford

The energy released by 2012?s Superstorm Sandy in the US was so immense that it triggered seismic waves which registered on equipment designed to detect earthquakes.
- By Tim Radford

An increasingly warm climate will mean ever more rapid changes in the Earth’s climatic zones, researchers say, and the species that live there will face a heightened extinction risk.
- By Tim Radford
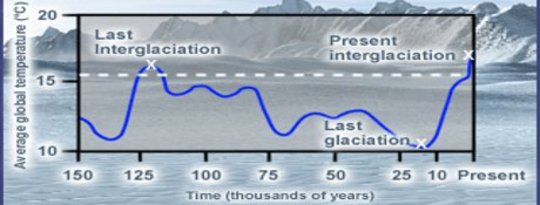
Work by an international scientific team has disclosed what the patterns of climate change have been across almost all the Earth’s continents over the past millennium. and sometimes longer.
- By Alex Kirby

Climate change is responsible for more than half the changes detected in the world’s vegetation, researchers say, and human activities for only about a third.

The authors found that heat waves are occurring more often, while cold waves have been decreasing. That shift is recognized to be in keeping with a warming climate.
- By R Jennings

The Arctic sea ice melt vigil has begun. Arctic melt is of great importance because it affects the climate of the planet in general and the weather of the northern latitudes in particular.
- By R Jennings
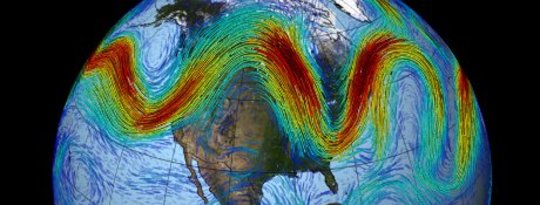
Be it in the oceans, on the land, or in the air and from the American breadbasket to the Siberian icy forests, to the land down under. global warming is occurring rapidly, right before our eyes.
- By R Jennings

Think the costs of global warming is something future generations will have to face? Think again. Whether it be drought in the US bread basket or intensified storms in the Northeast, it will cost you now, not later. From increased casualty insurance premiums to the price of strawberries, prepare to open your wallet a little wider.

What exactly does it mean for storms to get “stronger”? Does it mean faster winds? A larger wind field? Lower pressure at the center? More rain and snowfall? Higher storm surges?
- By R Jennings

Once upon a time the doctrine of man's dominion over the earth implied stewardship. Now many just call for an end to the EPA. If we continue on this course, it might mean an end to more than to the EPA. But really, ending the EPA is only about ending regulation so that the few can profit at the expense of the many.

According to Rebecca Lindsey of the National Climate Data Center the list of impacts from the U.S. drought seems endless. There have been record-low hay stocks, significant damage to house foundations, ethanol and beef processing plants idled, and mandatory water restrictions. In one Texas county alone there have been at least 25,000 dead pecan trees.