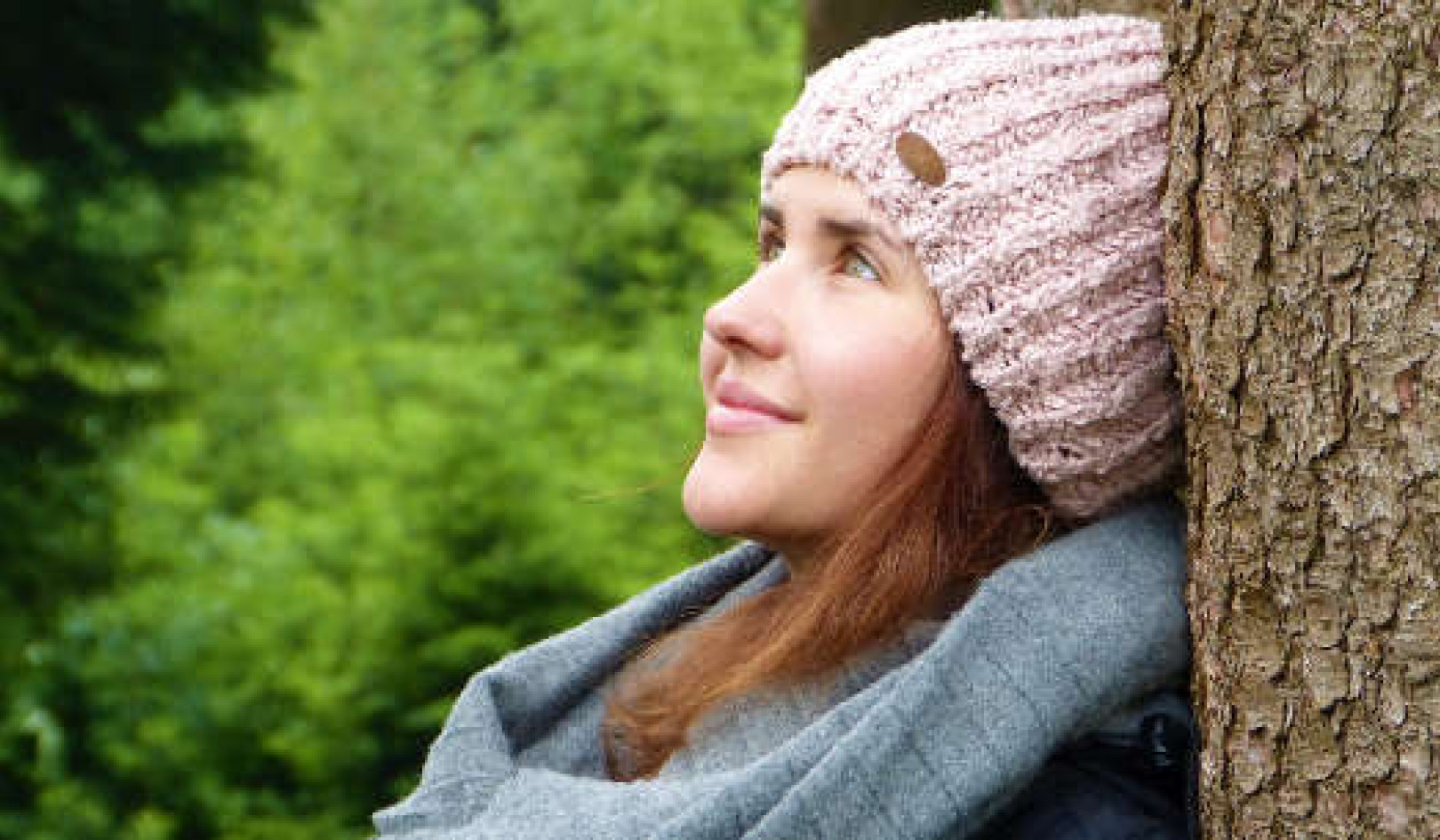
Rituals like hand-washing help spread hygiene practices that are essential to health and survival. Aditya Saputra/INA Photo Agency/Universal Images Group via Getty Images
Rituals like hand-washing help spread hygiene practices that are essential to health and survival. Aditya Saputra/INA Photo Agency/Universal Images Group via Getty Images
COVID-19 has disrupted many aspects of daily life, including rituals both sacred and mundane. At the same time, the pandemic has opened a unique opportunity globally to adapt rituals to meet new needs and respond to new challenges.
Rituals are social conventions that range from religious ceremonies like baptisms and bat mitzvahs to simple greetings like handshakes.
I study what rituals reveal about our minds, nature and culture. They are not arbitrary, capricious or random. Instead, they serve critical social functions such as welcoming newborns into families, celebrating graduations and marriages and mourning loved ones who’ve died. Rituals also promote solidarity by allowing communities to express their shared goals and values.
The pandemic has forced us to change many of our most common rituals, including how we celebrate rites of passage. Baby showers, birthday parties and funerals are now held virtually. Large celebratory signs on front lawns announce graduations. Couples livestream their virtual weddings on social media, and families host holiday celebrations outdoors to ensure social distancing.
Rituals around greetings and social support have also changed. Handshakes, kisses on the cheeks or lips and physical embraces have been replaced by elbow bumps, air kisses and virtual hugs.
 Secretary of Defense Lloyd Austin elbow bumps with Vice President Kamala Harris during his swearing-in ceremony at the White House. Doug Mills-Pool/Getty Images
Secretary of Defense Lloyd Austin elbow bumps with Vice President Kamala Harris during his swearing-in ceremony at the White House. Doug Mills-Pool/Getty Images
Managing uncertainty
During times of uncertainty and danger, people often use rituals to reduce their stress and exert control over their environment. That’s why rituals are common during periods of high risk, such as during pregnancy and after giving birth.
Consider Chhathi, a popular ritual in northeast India that takes place on the sixth day after a child’s birth. During the ritual ceremony, the mother and child are bathed and fed. Black thread is tied around the baby’s waist or wrist and black eyeliner is applied around the baby’s eyes. This is meant to provide protection from supernatural threats such as the evil eye. Chhathi initiates a new baby into the family, garners supernatural protection and reinforces social cohesion within the community.
A global pandemic is also a time of significant transition and uncertainty when people have greater need for physical and social support. Over the past year, people have used electronic media to rapidly transform routine social rituals. Like the in-person rituals they replaced, these new interactions – such as virtual happy hours, Zoom business meetings and distance-learning classrooms – strengthen social ties.
Societies also use rituals for practical reasons, such as improving health and avoiding illness. Records of rituals used in medicine date back to ancient Egypt and the Papyrus Ebers, one of the oldest known medical texts. It includes this ritual to treat blindness: Crush, powder and blend the two eyes of a pig, mineral eye salve, red oxide and wild honey in a clay bowl. Inject mixture into patient’s ear and say, “I have brought this thing and put it in its place. The crocodile god Sobek is weak and powerless.”
Contemporary rituals are also used in this way to attempt to treat and prevent illness. Rituals called simpatias are used to treat pulmonary ailments in Brazil, rituals based on traditional medicine are used to treat HIV in South Africa, rituals performed during pregnancy are used to prevent birth defects in India and rituals using homoeopathic remedies are used to treat rheumatoid arthritis in the U.K.
Promoting hygiene
Many religious rituals concern cleansing and purification. For example, it is obligatory for Muslims to wash their face, arms, head and feet before praying, a purification ritual called Wudu.
The COVID-19 pandemic has also prompted people to adopt new rituals around personal and communal hygiene such as wearing face masks in public, rigorously cleaning shared surfaces and taking turns being inside businesses and workplaces.
Anthropologists believe such rituals may be part of a hazard-precaution system, a psychological system geared toward responding to threats in the environment such as pathogens or contamination. Since reducing contamination and promoting hygiene is essential to health and survival, having rituals to spread these practices within a population is useful.
There are good reasons people spend time, money and energy engaging in rituals in the face of COVID-19 restrictions. They are essential to meeting our physical, social and psychological needs in the face of adversity.![]()
About The Author
Cristine H Legare, Professor of Psychology, The University of Texas at Austin College of Liberal Arts
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Related Books:
Atomic Habits: An Easy & Proven Way to Build Good Habits & Break Bad Ones
by James Clear
Atomic Habits provides practical advice for developing good habits and breaking bad ones, based on scientific research on behavior change.
Click for more info or to order
The Four Tendencies: The Indispensable Personality Profiles That Reveal How to Make Your Life Better (and Other People's Lives Better, Too)
by Gretchen Rubin
The Four Tendencies identifies four personality types and explains how understanding your own tendencies can help you improve your relationships, work habits, and overall happiness.
Click for more info or to order
Think Again: The Power of Knowing What You Don't Know
by Adam Grant
Think Again explores how people can change their minds and attitudes, and offers strategies for improving critical thinking and decision making.
Click for more info or to order
The Body Keeps the Score: Brain, Mind, and Body in the Healing of Trauma
by Bessel van der Kolk
The Body Keeps the Score discusses the connection between trauma and physical health, and offers insights into how trauma can be treated and healed.
Click for more info or to order
The Psychology of Money: Timeless lessons on wealth, greed, and happiness
by Morgan Housel
The Psychology of Money examines the ways in which our attitudes and behaviors around money can shape our financial success and overall well-being.