GRSI / shutterstock
The idea of a four-day working week is gaining traction. Recently, several high-profile companies have trialled reduced hours. And in the UK, the Labour Party has pledged a 32-hour four day work week within ten years should it come to power.
A number of research studies, including one by my colleagues and I, show clear benefits such as improvements in employee satisfaction and productivity, savings on commuter costs, and fewer days absent through sickness.
However, this wave of interest in a four-day week is no longer just about worker wellbeing – it is also about the environmental impact.
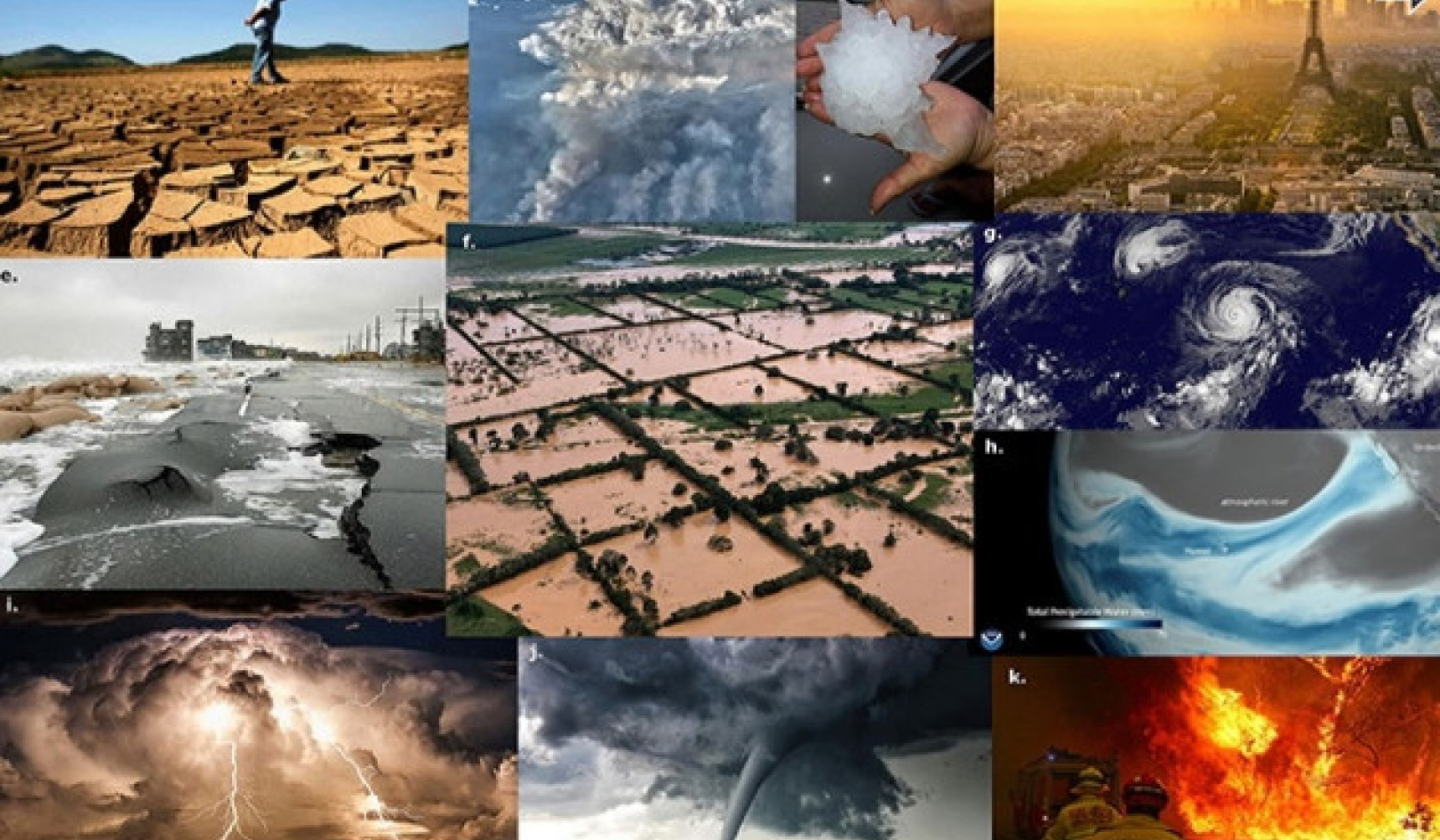
Several reports and commentators have identified various ways a four-day week could reduce our carbon footprint. Using data from 1970 to 2007 for 29 OECD member nations, a 2012 study found that a 10% reduction in work hours may lead to declines in ecological footprint, carbon footprint, and CO? emissions by 12.1%, 14.6% and 4.2% respectively.
Where would these savings come from? The most direct way a four-day week could cut emissions is by reducing carbon-intensive commutes, and our study indicated this has significant potential for a “green” dividend.

Unhealthy for people and planet. Jevanto Productions / shutterstock
Our research was based on a sample of 505 business leaders and owners, representing a variety of different sized organisations, and a separate sample of 2,063 adults, designed to reflect the UK in terms of age, gender and religion. We asked everyone how a four-day week would affect their commuting habits and then applied their answers to DfT National Road Traffic Survey data.
We found that, if we scaled up the results to apply to the UK, a national four-day working week would reduce the number of miles driven by employees travelling to work by 558 million each week. This in turn would reduce fuel consumption and travel costs. In this scenario, car mileage could reduce as much as 9%. More than half (51%) of employees said they would drive their car less, most commonly reducing weekly mileage by 10-19 miles.
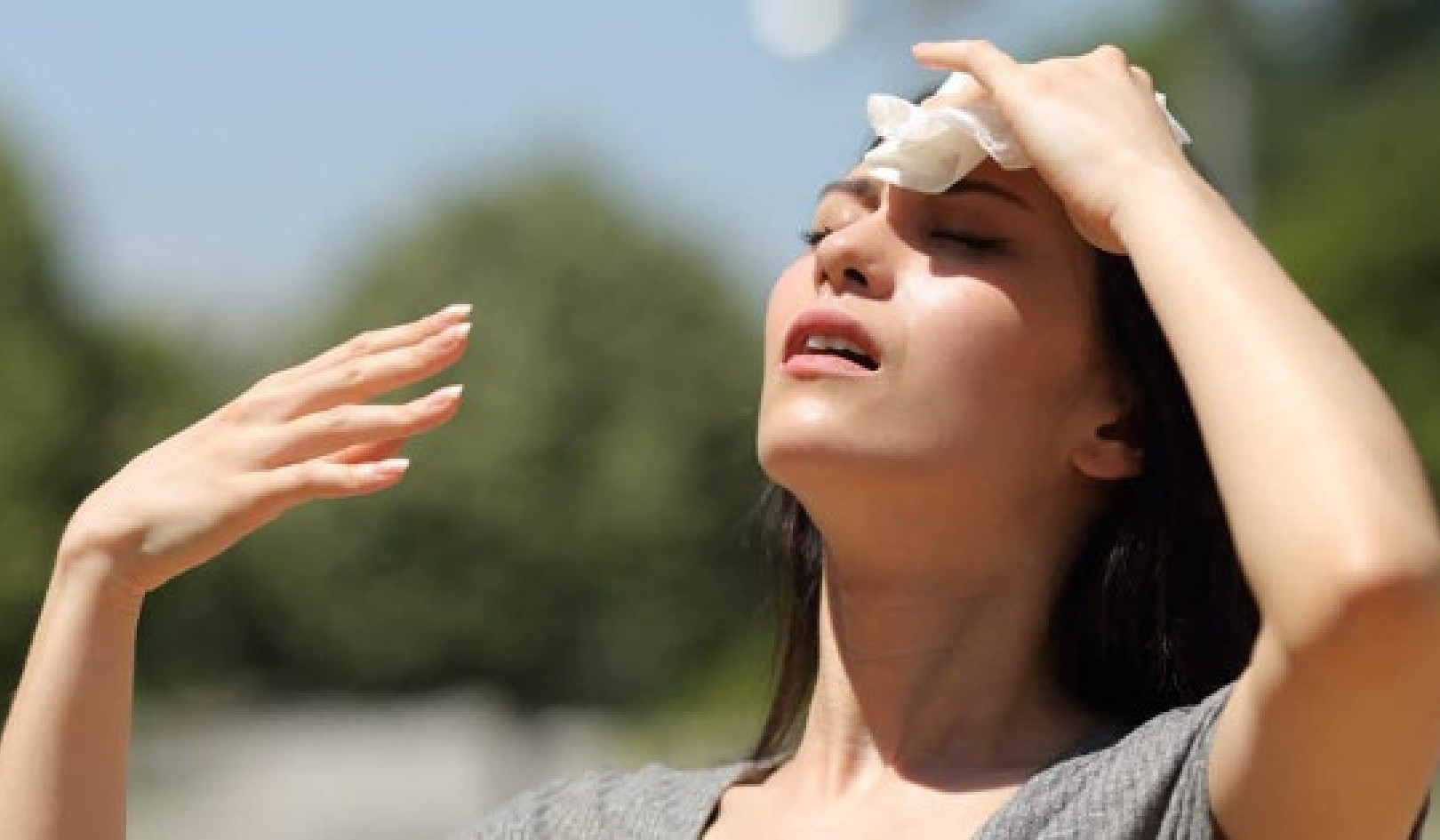
Less time spent in traffic is good news for other reasons: it can lead to health benefits, lowering the demand for carbon-intensive healthcare products and services such as hospital treatments, visits to GP or medications. Avoiding the stress and anxiety of a traffic jam is also good for mental health, especially among women.
With a three-day weekend, there are more opportunities for workers to exercise, spend time outdoors or do others things that improve their physical and mental health. This in turn means less demand for carbon-producing healthcare services.
Working one day less per week means less need for goods and services we use daily in the workplace. Computers and machinery will last longer, stationary and uniforms won’t need replacing as often, cleaners won’t need to work as much, and so on. There will be less need to produce these goods and services using carbon-intensive technologies and natural resources.
It’s potentially a virtuous cycle, as a better environment with less pollutants can improve productivity levels. Therefore, environmental benefits from four-day week can also be viewed as an investment in human capital.
It’s not entirely positive though
A four-day week can also have some negative environmental impacts. Policies and strategies are needed to minimise the adverse effects and maximise the “green” dividends.
Net benefits depend on how workers use the three-day weekend. If they use that extra day off to take a flight for a short break, drive a fancy sports car, or even to watch TV at home with the heating or air-conditioning cranked right up, then those fewer working hours could even be bad for the environment.

A shorter work week could lead to more long weekend holidays – by plane. MiniStocker / shutterstock
A four-day week may not achieve the full range of benefits if the work of five days is crammed into four days with longer hours (as happened in one experiment in the US state of Utah). Workers may have to prioritise tasks and work longer hours. This can cause anxieties, performance-related stress and an increase in demand for health services.
Unaffordable house prices across many parts of the UK, along with slow wage growth, means any loss of income due to a four-day week may force workers to top up their salaries with extra jobs. This would negate the environmental benefits of that supposed day off.
What needs to be done?
New technologies such as artificial intelligence and robotics can lead to productivity gains, and we need to utilise this wisely if a four-day week is to achieve the same output as the standard five days without job or income losses.
If workers are to spend their extra free time boosting their health and wellbeing, then we’ll also need further investments into less carbon-intensive infrastructures. That means better public transport, more parks, libraries, community centres, sports facilities.
It is crucial that workers understand the full range of issues of four-day weeks. Organisations should invest and provide support, and appropriate training programmes should be rolled out.
Finally, workers must be willing to change their perspectives and make positive behavioural changes. This would make the four-day week concept work for them, their families, their employers and for the environment.
About The Author
Anupam Nanda, Professor of Urban Economics and Real Estate, Henley Business School, University of Reading
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Related Books
Drawdown: The Most Comprehensive Plan Ever Proposed to Reverse Global Warming
by Paul Hawken and Tom Steyer In the face of widespread fear and apathy, an international coalition of researchers, professionals, and scientists have come together to offer a set of realistic and bold solutions to climate change. One hundred techniques and practices are described here—some are well known; some you may have never heard of. They range from clean energy to educating girls in lower-income countries to land use practices that pull carbon out of the air. The solutions exist, are economically viable, and communities throughout the world are currently enacting them with skill and determination. Available On Amazon
In the face of widespread fear and apathy, an international coalition of researchers, professionals, and scientists have come together to offer a set of realistic and bold solutions to climate change. One hundred techniques and practices are described here—some are well known; some you may have never heard of. They range from clean energy to educating girls in lower-income countries to land use practices that pull carbon out of the air. The solutions exist, are economically viable, and communities throughout the world are currently enacting them with skill and determination. Available On Amazon
Designing Climate Solutions: A Policy Guide for Low-Carbon Energy
by Hal Harvey, Robbie Orvis, Jeffrey Rissman With the effects of climate change already upon us, the need to cut global greenhouse gas emissions is nothing less than urgent. It’s a daunting challenge, but the technologies and strategies to meet it exist today. A small set of energy policies, designed and implemented well, can put us on the path to a low carbon future. Energy systems are large and complex, so energy policy must be focused and cost-effective. One-size-fits-all approaches simply won’t get the job done. Policymakers need a clear, comprehensive resource that outlines the energy policies that will have the biggest impact on our climate future, and describes how to design these policies well. Available On Amazon
With the effects of climate change already upon us, the need to cut global greenhouse gas emissions is nothing less than urgent. It’s a daunting challenge, but the technologies and strategies to meet it exist today. A small set of energy policies, designed and implemented well, can put us on the path to a low carbon future. Energy systems are large and complex, so energy policy must be focused and cost-effective. One-size-fits-all approaches simply won’t get the job done. Policymakers need a clear, comprehensive resource that outlines the energy policies that will have the biggest impact on our climate future, and describes how to design these policies well. Available On Amazon
This Changes Everything: Capitalism vs. The Climate
by Naomi Klein In This Changes Everything Naomi Klein argues that climate change isn’t just another issue to be neatly filed between taxes and health care. It’s an alarm that calls us to fix an economic system that is already failing us in many ways. Klein meticulously builds the case for how massively reducing our greenhouse emissions is our best chance to simultaneously reduce gaping inequalities, re-imagine our broken democracies, and rebuild our gutted local economies. She exposes the ideological desperation of the climate-change deniers, the messianic delusions of the would-be geoengineers, and the tragic defeatism of too many mainstream green initiatives. And she demonstrates precisely why the market has not—and cannot—fix the climate crisis but will instead make things worse, with ever more extreme and ecologically damaging extraction methods, accompanied by rampant disaster capitalism. Available On Amazon
In This Changes Everything Naomi Klein argues that climate change isn’t just another issue to be neatly filed between taxes and health care. It’s an alarm that calls us to fix an economic system that is already failing us in many ways. Klein meticulously builds the case for how massively reducing our greenhouse emissions is our best chance to simultaneously reduce gaping inequalities, re-imagine our broken democracies, and rebuild our gutted local economies. She exposes the ideological desperation of the climate-change deniers, the messianic delusions of the would-be geoengineers, and the tragic defeatism of too many mainstream green initiatives. And she demonstrates precisely why the market has not—and cannot—fix the climate crisis but will instead make things worse, with ever more extreme and ecologically damaging extraction methods, accompanied by rampant disaster capitalism. Available On Amazon
From The Publisher:
Purchases on Amazon go to defray the cost of bringing you InnerSelf.comelf.com, MightyNatural.com, and ClimateImpactNews.com at no cost and without advertisers that track your browsing habits. Even if you click on a link but don't buy these selected products, anything else you buy in that same visit on Amazon pays us a small commission. There is no additional cost to you, so please contribute to the effort. You can also use this link to use to Amazon at any time so you can help support our efforts.