PopTika/Shutterstock
In mid November 2020, South Dakota emergency room nurse Jodi Doering tweeted her experience of caring for dying patients.
Many, she said, were denying the existence of COVID-19 until their final breaths.
Their last dying words are “this can’t be happening, it’s not real.” And when they should be … FaceTiming their families, they’re filled with anger and hatred
Five months earlier, a 30 year old man died of COVID-19 in the Methodist Hospital in San Antonio, Texas. His dying words, to his nurse:
I think I made a mistake. I thought this was a hoax, but it’s not
The hospital’s chief medical officer reported that the patient became infected at a party with other sceptics, all thinking the virus was “fake news”.
Trust varies by location
That Texas party was doubtless organised by mobile phone, and the friends drove their cars there. Both pieces of technology have much more computer storage and processing power than the Apollo 11 moon landing had in 1969.
Ironically, recent advances in science and technology helped people gather to express their doubts about scientific advice.
But it is not just individuals who have downplayed scientific advice and warnings about the virus.
Scientists around the world frequently feel governments do not pay enough attention to scientific advice. That was the view of some half of the 25,307 researchers surveyed by Frontiers, a Swiss publisher of scientific journals, in May and June.
New Zealand takes advice, the US not so much
The survey asked the international scientists whether lawmakers in their country had used scientific advice to inform their COVID strategy.
Overall, the scientists split 50:50 on how much, or how little, their government had considered the scientific advice.
Opinions varied widely between countries. In New Zealand, almost 80% were happy with the attention their government paid to scientific advice. In the United States, fewer than 20% of the scientists thought the same about their government.
Where policy makers take scientific advice into account
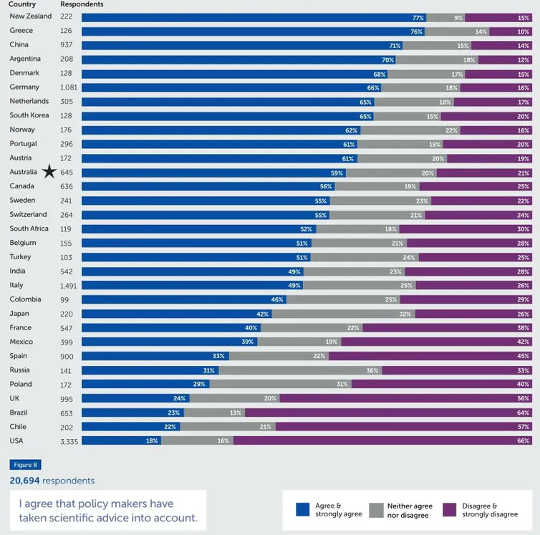
The Academic Response to COVID-19, Frontiers in Public Health, October 2000
One obvious factor in scientists’ attitudes is the penchant some politicians from various parts of the world have for denigrating experts.
Outgoing US President Donald Trump frequently dismisses anything he disagrees with as “fake news”.
In Britain in the 2016 Brexit referendum, a raft of economists argued that Brexit would damage the UK economy. Leading Conservative politician and Brexit supporter Michael Gove ignored them, saying: “people in this country have had enough of experts”.
And recently in Australia, the Grattan Institute, an independent think tank, issued a report Flame Out, which argued there is limited future need for natural gas.
A spokesman for the energy minister Angus Taylor dismissed the report, saying its findings about the manufacturing sector did not reflect the industry’s own views.
Who needs experts when they can rely on industry?
Less-equal societies trust less
But there are other, less obvious, factors underlying how much attention countries and governments have paid to expert advice.
A significant one is the level of inequality in the country. This graph maps the results from the Frontiers survey against levels of income inequality.
Inequality is measured by the standard Gini coefficient, which runs from 0.0 (everyone has the same income) to 1.0 (one person has all of a country’s income).
Proportion of scientists saying government took scientific advice on COVID
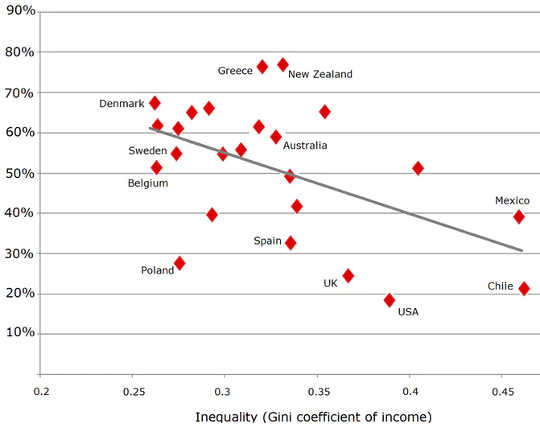
Gini coefficient measures inequality on scale where 0 = income is shared equally, 1 = one person has all the income. Frontiers in Public Health, OECD
The line running through the diamonds is a trend line. It shows that, on average, trust in science declines as inequality increases.
On average, an increase of one percentage point in inequality is associated with a decrease of 1.5 percentage points in listening to scientists.
Richard Wilkinson and Kate Pickett provide an clue as to why this might be the case in their 2009 book The Spirit Level, observing that
inequality affects how you see those around you … people in less equal societies are less likely to trust each other".
In such countries the beliefs that it’s a “dog-eat-dog” world, or that “everyone’s out for themselves”, seem to be more prevalent.
New York Times columnist David Brooks believes collapsing levels of trust are devastating America. In his view
an anti-institutional bias has manifested itself as hatred of government; an unwillingness to defer to expertise, authority, and basic science; and a reluctance to fund the civic infrastructure of society, such as a decent public health system.
World-wide, efforts to tackle the coronavirus have been hampered by communities disputing the severity – or even the existence – of the virus.
Australia still has a fair measure of trust. Announcing restrictions earlier this year, Victorian Premier Dan Andrews said “everybody will pay a price” if Victorians don’t play their part and act on the advice of experts.
So far we have, impressively; and in Sydney too. But trust is fragile.
Inequality is a corrosive solvent.
About the Author
Tony Ward, Fellow in Historical Studies, University of Melbourne
This article is republished from The Conversation under a Creative Commons license. Read the original article.
Books on Inequality from Amazon's Best Sellers list
"Caste: The Origins of Our Discontents"
by Isabel Wilkerson
In this book, Isabel Wilkerson examines the history of caste systems in societies around the world, including in the United States. The book explores the impact of caste on individuals and society, and offers a framework for understanding and addressing inequality.
Click for more info or to order
"The Color of Law: A Forgotten History of How Our Government Segregated America"
by Richard Rothstein
In this book, Richard Rothstein explores the history of government policies that created and reinforced racial segregation in the United States. The book examines the impact of these policies on individuals and communities, and offers a call to action for addressing ongoing inequality.
Click for more info or to order
"The Sum of Us: What Racism Costs Everyone and How We Can Prosper Together"
by Heather McGhee
In this book, Heather McGhee explores the economic and social costs of racism, and offers a vision for a more equitable and prosperous society. The book includes stories of individuals and communities who have challenged inequality, as well as practical solutions for creating a more inclusive society.
Click for more info or to order
"The Deficit Myth: Modern Monetary Theory and the Birth of the People's Economy"
by Stephanie Kelton
In this book, Stephanie Kelton challenges conventional ideas about government spending and the national deficit, and offers a new framework for understanding economic policy. The book includes practical solutions for addressing inequality and creating a more equitable economy.
Click for more info or to order
"The New Jim Crow: Mass Incarceration in the Age of Colorblindness"
by Michelle Alexander
In this book, Michelle Alexander explores the ways in which the criminal justice system perpetuates racial inequality and discrimination, particularly against Black Americans. The book includes a historical analysis of the system and its impact, as well as a call to action for reform.